What is Access Control System? Definition, Key Components, Tailgating Prevention
This article explains what an access control system is, its key components, and common authentication methods. It also highlights security gaps such as tailgating and introduces effective prevention measures, including OPTEX’s advanced anti-tailgating solution.
What is Access Control System? Definition and Importance
Access Control System is a security system designed to manage and restrict entry and exit to buildings, facilities, or specific areas. By ensuring that only authorized individuals can access designated locations, it reduces the risk of information leaks and unauthorized entry, safeguarding lives, property, and sensitive data.
A typical access control system consists of two main processes: Authentication and Authorization.
- Authentication: Verifying identity using methods such as cards, PIN codes, fingerprints, or facial recognition.
- Authorization: Determining whether the individual has permission to enter a specific area.
Once authorization is confirmed, the system unlocks electric locks or security gates. This system is not merely a replacement for traditional keys — it provides the ability to accurately record and manage who accessed, when, and where, which is a key feature.
Access control systems are widely implemented in office buildings, research facilities, data centers, hospitals, airports, and other locations, making them essential for enforcing security policies and ensuring compliance.
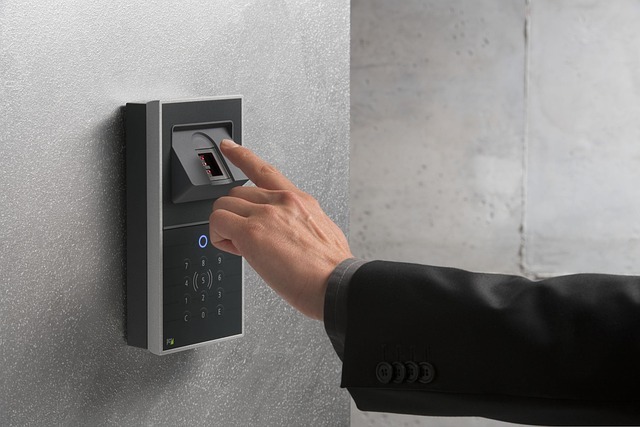

Main Components of an Access Control System
An access control system manages entry and exit through the integration of authentication devices, controllers, and gate mechanisms.
1. Authentication Devices
These devices verify a user’s access rights. The user inputs authentication information (such as an ID card, PIN code, or fingerprint) into the device. Common examples include card readers, PIN pads, and biometric scanners.
2. Controller
The controller analyzes the information read by the authentication device, determines whether access should be granted, and controls the electric lock. It receives data from the authentication device, compares it with pre-registered information, and if it matches, sends an “unlock” signal to the electric lock.
3. Door and Gate Mechanisms
These include electric locks, automatic doors, and security gates. They receive signals from the authentication system and physically open or close the lock.
Types of Authentication in Access Control Systems
The authentication method in an access control system is a critical factor that determines the system’s reliability and flexibility. It is selected based on the required security level and operational environment. The main types include:
● Card Authentication

The most common method, typically used for employee ID cards or entry passes. Authentication is performed by reading the card with a reader, but there is a risk of lending, borrowing, or loss.
● PIN Code Authentication

A method that users enter a numeric passcode. It is cost-effective and suitable for basic security, but there is a risk of the code being shared, so regular updates are recommended.
● Biometric Authentication
Uses fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans. Unlike card authentication, there is no risk of loss. However, if the authentication criteria are too strict, even authorized users may be denied access; if too lenient, unauthorized users may gain access.
● Multi-Factor Authentication
To strengthen security, Multi-Factor Authentication can be implemented by combining multiple methods, such as using ID card together with a PIN code.
Security Gaps in Access Control: The Problem of Tailgating
One of the weaknesses of an access control system is the risk of tailgating that occurs after authentication. An access control system is designed to allow only authorized individuals to enter a facility after completing the authentication process. However, regardless of the authentication method used, the risk of tailgating remains.
Tailgating refers to a situation where an unauthorized person follows an authenticated individual into a secured room. This can happen not only in cases of malicious intent but also during busy periods, such as when doors remain open for extended times during rush hours, allowing people to pass through without authentication. In any case, it increases security risks.

Examples of methods to prevent tailgating include:
- Gate devices combined with entry management systems for one-person passage control
By linking security gates with entry management systems, it is possible to regulate passage one person at a time. In common areas with lower security levels, processing speed is prioritized, while in high-security areas, strict passage control is required. - Alarm-based tailgating prevention
Measures using sensors or active tags are effective when installing security gates is difficult.
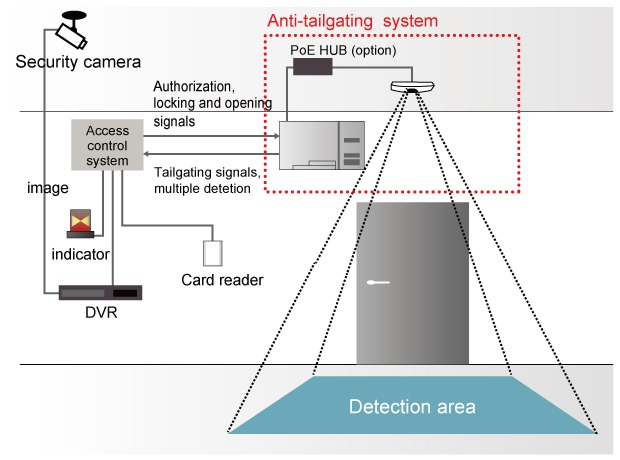
OPTEX offers a tailgating prevention system that uses image sensing technology with cameras.
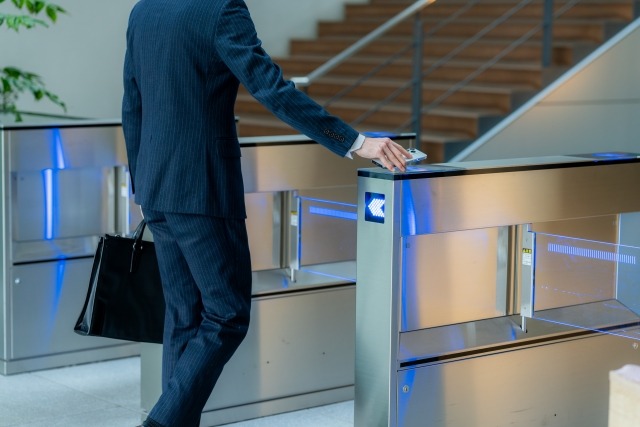

OPTEX’s Anti-Tailgating System Solution
Even with access control system in place, the risk of tailgating remains. To address this challenge, OPTEX offers the ACCURANCE OV-102 series, a camera-based tailgating detection system that uses proprietary image-sensing technology to analyze human shapes and movements in real time. It detects unauthorized individuals following an authenticated person and prevents unauthorized access to secured areas.
For more details, please visit → https://optex-asean.com/solution/anti-tailgating-system/
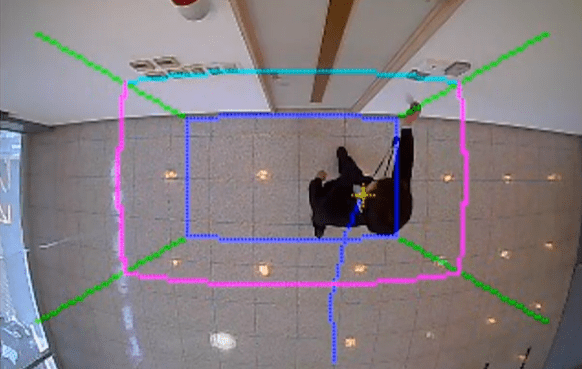
Basic Functions
- Signal output when tailgating is detected
- Do not unlock the door if multiple people are detected within the monitored area in front of the door
- Integration with sirens, warning lights, and surveillance camera systems via access control system
Key Features
- Easy installation and smooth integration: Ceiling-mounted, no internet required, setup via web browser
- Adaptable to various environments: Unaffected by changes in lighting. Door cancellation function
- Privacy-conscious: No recording function
- Flexible connectivity: I/O relay output for integration with various access control devices
Examples of Tailgating Scenarios That Can Be Prevented
- An unauthorized person enters right after an authenticated individual
- Multiple people enter at once, making it unclear who was actually authenticated
- Visitors or contractors accompany employees into a secured area without being recorded
Understand OPTEX Anti-Tailgating System Through Video
Summary: Strengthening Your Access Control System
Access control system is a fundamental solution for protecting facility security, but the risk of tailgating remains even after authentication. To enhance security, a dual approach combining authentication with tailgating detection and prevention is highly effective.
OPTEX’s anti-tailgating system is designed to address this challenge, preventing unauthorized entry through real-time detection, alerts, and door control.
For detailed specifications and implementation guidance, please feel free to contact OPTEX Thailand.
Contact OPTEX
Please feel free to contact us for further information.
We are always eager to support you and propose a solution that suits your needs.









